What is ggscout?
GitGuardian Scout (ggscout) is a command-line application that collects secrets and their metadata from your Secrets Managers and synchronizes this data with your GitGuardian platform.
Why Collect Secrets?
When a secret is leaked in your code repository or exposed in your infrastructure, a critical question arises: Is this secret currently in use, and where? Without an inventory of your production secrets, answering this question is time-consuming and error-prone.
ggscout solves this problem by:
- Creating an inventory of secrets stored in your Secrets Managers (HashiCorp Vault, AWS Secrets Manager, etc.)
- Hashing these secrets locally using the HMSL algorithm - secrets never leave your infrastructure in clear text
- Reconciling this inventory with secrets detected by GitGuardian in your codebase or other sources
This reconciliation enables three key capabilities:
1. Extend Detection Coverage
By maintaining an inventory of vaulted secrets, you can detect when these secrets are compromised elsewhere in your perimeter. When GitGuardian detects a leaked secret, it can immediately tell you if it matches a secret currently stored in your vault.
Example: A developer accidentally commits an API key to a public repository. With ggscout, you instantly know this key is from your production HashiCorp Vault and which application uses it.
2. Improve Incident Prioritization
Vaulted secrets come with valuable metadata: vault paths, lease times, rotation policies, associated applications, and environments. This context helps you prioritize which incidents to remediate first.
Example: Two secrets are leaked. One has a 90-day lease and is only used in a development environment. The other has a 365-day lease and is used by a production payment service. The metadata from ggscout helps you prioritize the production secret first.
3. Bootstrap Incident Remediation
By identifying secrets that are not in your vault (unvaulted secrets), ggscout can help you secure them. It can automatically push unvaulted secrets into your Secrets Manager, providing your developers with the vault path to update their code.
Example: GitGuardian detects a hardcoded database password in an old repository. Using ggscout, you can push this secret to your vault and provide developers with the exact path to reference it, streamlining the remediation process.
Secrets values will never leave your environment in clear!
Secrets values are hashed using the HMSL hashing algorithm before they are sent to your GitGuardian workspace. Other non-sensitive metadata like the secret names, paths in the vault, creation date, lease time, etc... are also collected to help you in the remediation process.
Safely collect secrets to ease incident remediation
Once you deployed and configured ggscout in your environment, it runs as follows:
- It collects the secrets and associated metadata from the Secrets Managers you configured.
- It hashes the secrets using the HMSL hashing algorithm.
- It sends the collected data to GitGuardian and reconciles it with existing secrets incidents.
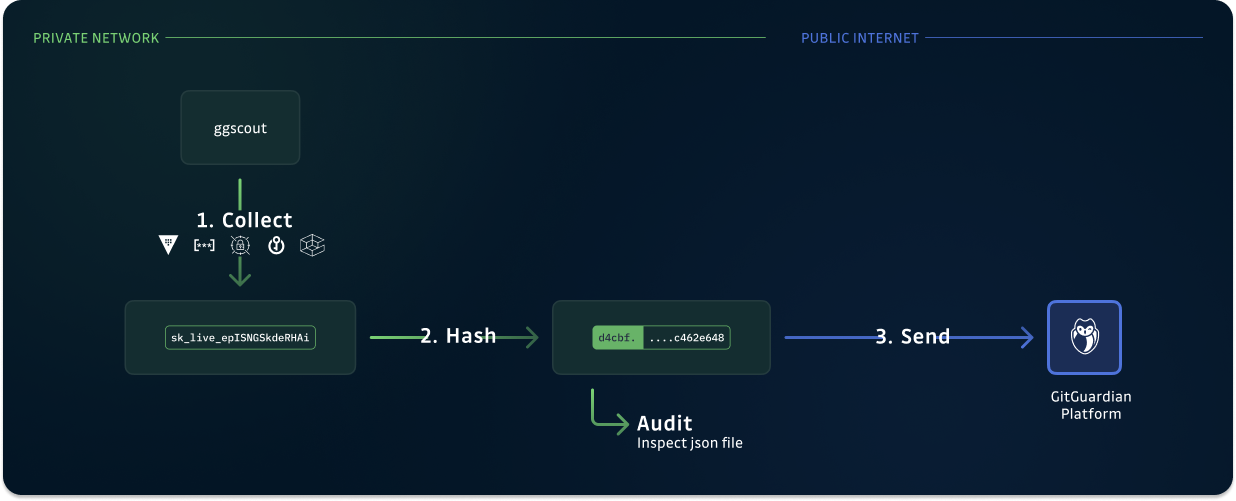
That’s it, you can start leveraging these capabilities from your GitGuardian Platform!
Safely store unvaulted secrets
With ggscout, you will be able to identify unvaulted secrets from your incidents list.
What’s more, you will also be able to push these secrets to your Secret Managers and bootstrap the remediation of these incidents!
Here is the standard scenario:
- Once a secret incident is prioritized, you can insert the secret within your Secrets Manager
- Your developers fix their code by properly invoking the secret from the right path provided in the Secret Incident detail
- Once the code fixing is done, revoke the right secret from the vault using the hyperlink provided in the Secret Incident detail
ggscout supports this entire process using the following simple flow:
- ggscout retrieves the secret incident that has not yet been vaulted.
- ggscout writes the secret to the specified location.
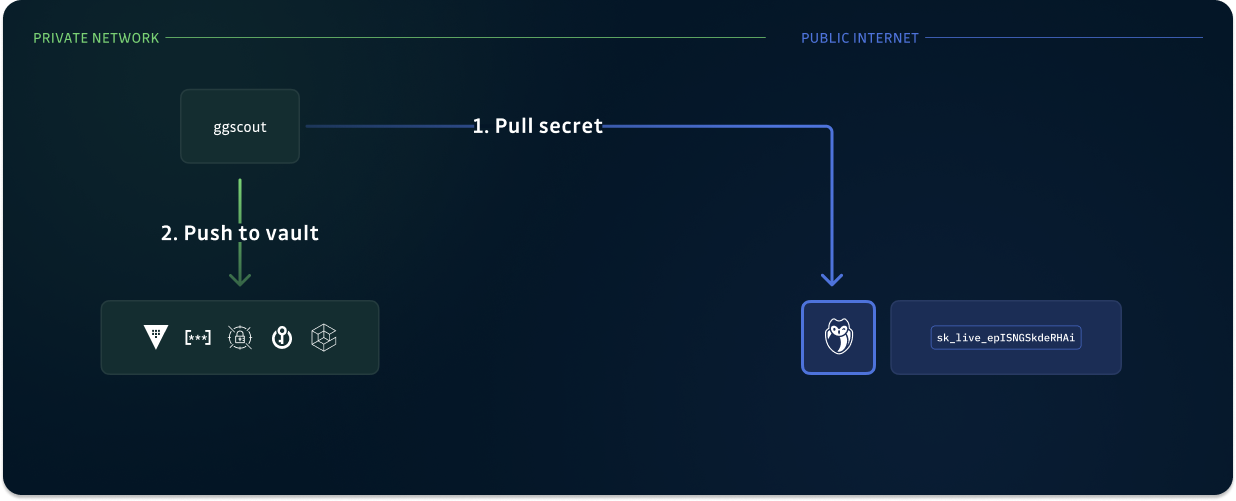
You can choose not to grant write access.
You can also restrict the locations where the scout can write secrets (e.g., a temporary path specific to ggscout).
Keep full authority on ggscout execution
No sensitive information ever leave your infrastructure.
Having an external program like ggscout allows you to:
- Have your team control its execution and accesses (e.g. having partial accesses, having one instance for read access and another for write access)
- Have your team monitor what data is being processed
ggscout is auditable.
- You can run the fetch-only mode and write a JSON report on your disk so that you can audit the data collected by ggscout, and ensure no secret values in clear are collected. The data available in the report is exactly the data sent to the GitGuardian in default mode.
- You can request access to the source code
Getting Started
Ready to try ggscout? Head over to the Deploy and configure ggscout page, which includes a Quick Start guide for local testing with the CLI binary or Python package, as well as production deployment options using Docker or Kubernetes.
No GitGuardian Platform Access?
If you are deploying ggscout in a Kubernetes cluster but lack access to the GitGuardian platform, preventing you from sending the hashed secrets, ggbridge is the solution. It establishes a secure, mTLS-authenticated gateway between your network and the GitGuardian platform, enabling ggscout to communicate with the GitGuardian public API and transmit the inventory data.
For detailed setup instructions and additional information, please refer to the ggbridge documentation.

