Pre-receive
Prelude
A pre-receive hook allows you to reject commits from being pushed to a git repository if they do not validate every check. Please refer to our learning center for more information.
GitGuardian pre-receive hook is performed through our CLI application ggshield. ggshield is a wrapper around GitGuardian API for secrets detection that requires an API key to work.
Since pre-receive hooks are configured to run programmatically on the VCS instance, we recommend the use of a dedicated service account to authenticate ggshield calls. To create a service account, sign in to your GitGuardian workspace and go to the API section.
You can find ggshield's pre-receive hook samples in the doc/pre-receive.sample and doc/pre-receive-docker.sample.
GitGuardian supports pre-receive hooks on GitHub Enterprise Server, but GitHub enforces a 5-second timeout for push evaluations. If the evaluation exceeds this limit, the push is rejected. This may affect the reliability of the pre-receive hook. For more details, see GitHub's pre-receive hooks documentation.
Preview
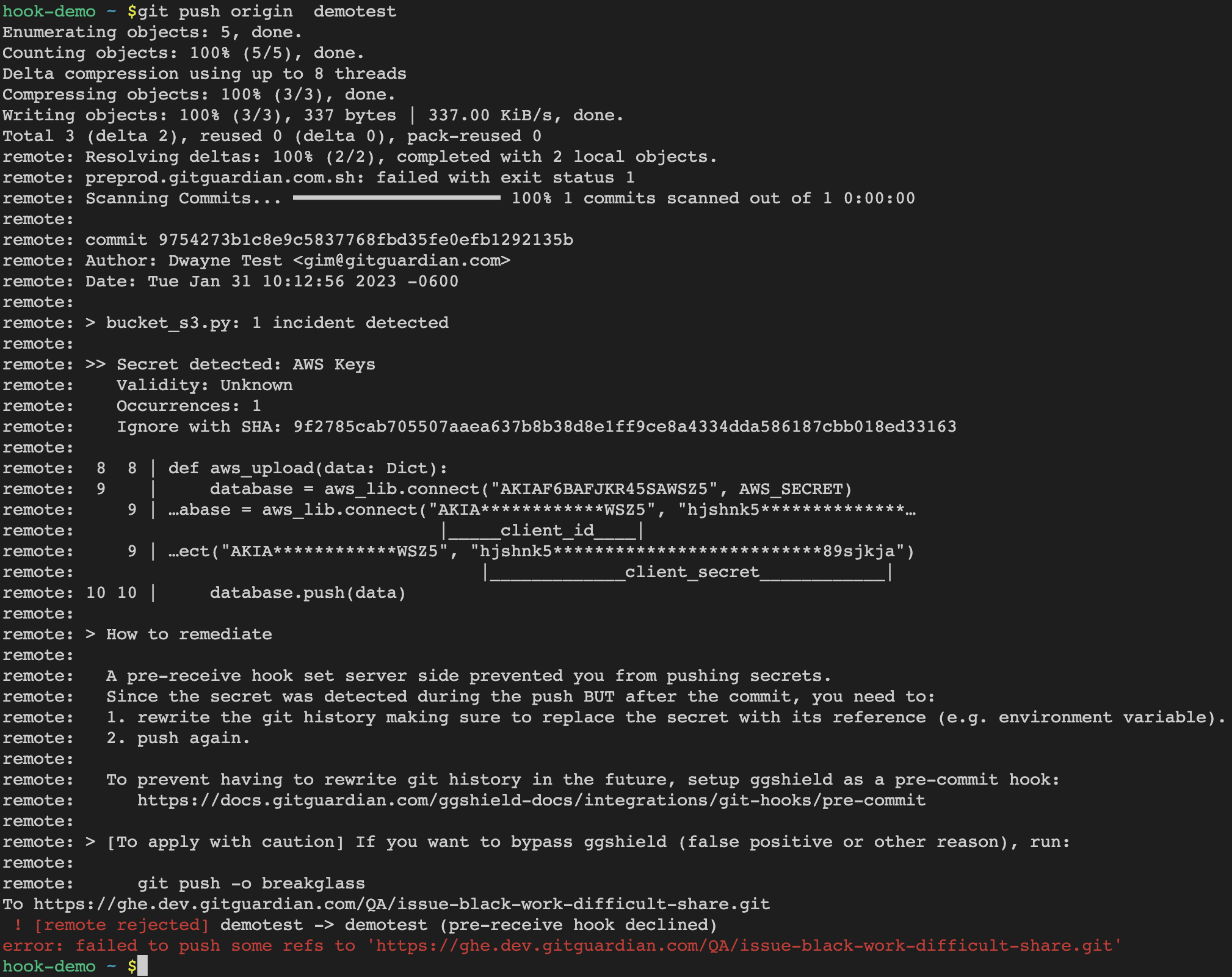
Customize the remediation message and add your own to offer developers precise guidance for resolving their code issues and continuing their work.
Gitlab Self-Managed and Bitbucket Server
Install ggshield git pre-receive hook
The sample script can be found in pre-receive.sample.
-
This pre-receive hook requires the host machine to have python>=3.8 and pip installed
-
Install
ggshieldfrom pip:pip install ggshield -
Move
pre-receive.sampleto.git/hooks/pre-receiveor to your provider's git hook directory -
Mark the script executable with
chmod +x .git/hooks/pre-receive -
Define the
GITGUARDIAN_API_KEYenvironment variable. Either in a machine wide configuration file or in the.git/hooks/pre-receivefile, as instructed in the sample file.
Install ggshield git pre-receive hook with Docker
For the pre-receive hook to work, the directory where the repositories are stored must also be mounted on the container.
The sample script can be found in pre-receive-docker.sample
This pre-receive hook requires the host machine to have Docker installed.
- Download the script as
.git/hooks/pre-receive:curl -L https://github.com/GitGuardian/ggshield/raw/main/doc/pre-receive-docker.sample > .git/hooks/pre-receive - Make it executable:
chmod +x .git/hooks/pre-receive - Either define
GITGUARDIAN_API_KEYas a machine-wide environment variable or set it in the.git/hooks/pre-receiveas instructed in the sample file.
GitHub Enterprise Server
The minimum GitHub Enterprise Server version required to support pre-receive hooks is 3.14.
Installing a git pre-receive hook on GitHub Enterprise Server requires 2 components:
- an environment to execute the script in,
- a script executed for each push event.
For more information, visit GitHub Enterprise Server documentation about pre-receive hook.
The pre-receive environment
A pre-receive hook environment is a Linux chroot. We provide the create-ghe-environment script to create a ready-to-upload archive of a pre-receive environment.
This script must be run on a Linux machine with Docker installed. Here is how to use it:
- Clone the ggshield repository:
git clone https://github.com/GitGuardian/ggshield.git
cd ggshield - Make sure the
GITGUARDIAN_API_KEYenvironment variable contains your API key. - Run the script:
./scripts/create-ghe-environment 3.14
When the script is done, it should print a message like this:
create-ghe-environment: Storing chroot in ggshield-ghe-3.14.tar.gz
You can now upload this file to the GitHub Enterprise Server and add it using the following command:
ghe-hook-env-create ggshield-environment ~/ggshield-ghe-3.14.tar.gz
Or you can upload this file to a server and pass its URL to the GitHub Enterprise Server web user interface to add it.
Script
You need to add the following script to a repository hosted in the GitHub Enterprise Server:
#!/bin/bash
# If you don't use the SaaS product, you need to setup your onprem public api url:
# export GITGUARDIAN_API_URL=<your onprem public api url>
export GITGUARDIAN_API_KEY=$(cat /app/api_key)
/app/.venv/bin/ggshield secret scan pre-receive
This script file should have execute permission.
Since the script name appears in the pre-receive hook result, we recommend to name it pre-receive.sh.
Create the pre-receive hook
You are now able to follow GitHub Enterprise Server documentation to create the pre-receive hook.
Skipping the pre-receive hook
ggshield's pre-receive hook can be skipped by adding -o breakglass to the git push command.
For the -o breakglass option to be taken into account, the remote repository must have the receive.advertisePushOptions git configuration option turned on.
This option can be turned on by running the following command on the server side:
git config receive.advertisePushOptions true
Some Git hosting services enable this option globally by default. Others do not.
FAQ
How do I avoid getting alerts for secrets already detected on the GitGuardian dashboard?
We recommend you use the option --ignore-known-secrets on the pre-receive hook. In this case, ggshield will not trigger any alerts, after you run a git push, for secrets that are already known by the GitGuardian dashboard (detected in previous commits and pull or merge requests).
All known secrets will be ignored, in the commits pushed and the merge/pull request, including those that were hardcoded by other developers.
- To enable this option, replace the following in the pre-receive hook
with:
ggshield secret scan pre-receiveggshield secret scan pre-receive --ignore-known-secrets
How do use a custom config for this pre-receive hook?
-
Create a
gitguardian.yamlsomewhere in the system. An example config file is available here. -
Replace in the pre-receive hook
ggshield secret scan pre-receivewith:
ggshield -c <INSERT path to gitguardian.yaml> secret scan pre-receive

