Monitor Bitbucket Cloud repositories for exposed secrets in source files, configuration files, and commit histories.
Why Monitor Bitbucket Cloud?
Bitbucket Cloud workspaces contain countless repositories where developers inadvertently commit sensitive credentials. These hardcoded secrets become permanently embedded in git history, creating persistent security vulnerabilities that can be discovered and exploited by unauthorized users, potentially leading to complete system compromise.
Capabilities
| Feature | Support | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Historical Scanning | ✅ (Supported) | Complete repository history analysis |
| Real-time Detection | ✅ (Supported) | Instant detection via webhooks |
| Monitored Perimeter | ✅ (Supported) | Granular monitoring of your Orgs and repos |
| Team Perimeter | ✅ (Supported) | Team-based access control |
| Presence Check | ✅ (Supported) | Verify if secrets are still accessible |
| File Attachments | ❌ (Not Supported) | Not applicable for code repositories |
What we scan:
- Source code files, configuration files, and raw text files
- All repository branches and commit history
Setup
Prerequisites:
- Owner or Manager account on your GitGuardian Dashboard
- Bitbucket Workspace Owner permissions for the workspaces you want to monitor
GitGuardian integrates with your Bitbucket Cloud workspace using an API token. For more details on API tokens, refer to the Bitbucket Cloud documentation.
Create an API token
The API token must be generated by the Workspace Owner of the workspace(s) you intend to monitor. This grants the necessary permissions to automatically create the required webhooks.
-
Log in to Bitbucket Cloud as the Workspace Owner;
-
Navigate to the Profile and visibility within the Atlassian account settings;
-
Get the email address in the Bitbucket profile settings
-
On the Atlassian account page, navigate to the API tokens section within the security settings;
-
Click on "Create API token with scopes" to start the creation of your API token. Use a simple name such as "GitGuardian". We recommend you set the expiration date to 1 year, this is the maximum allowed.
-
On the "Select app" page, select "Bitbucket".
-
On the "Select scopes" assign the following scopes:
- read:project:bitbucket
- delete:webhook:bitbucket
- read:webhook:bitbucket
- write:webhook:bitbucket
- read:repository:bitbucket
- read:user:bitbucket
- read:workspace:bitbucket
- read:permission:bitbucket
-
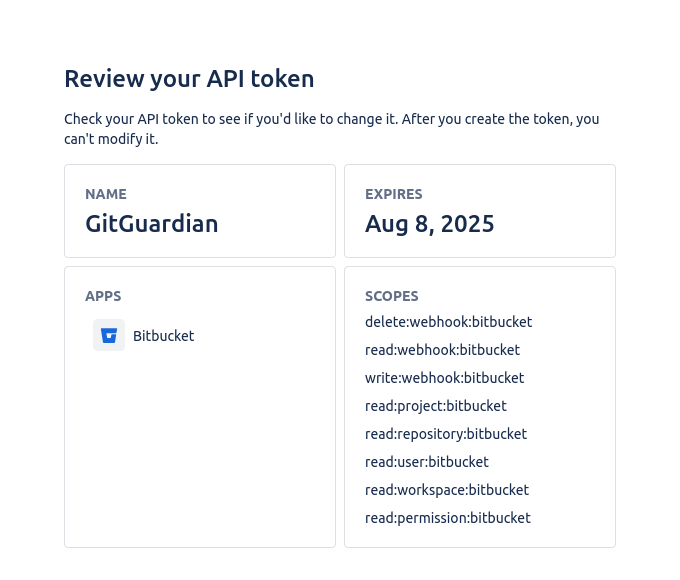
On the final "Create token page", recheck that the scopes are correct:
-
Get the API token
Integrate your Bitbucket workspaces with GitGuardian
-
Navigate to Settings > Integrations > Sources.
-
Click on Install for Bitbucket Cloud.
-
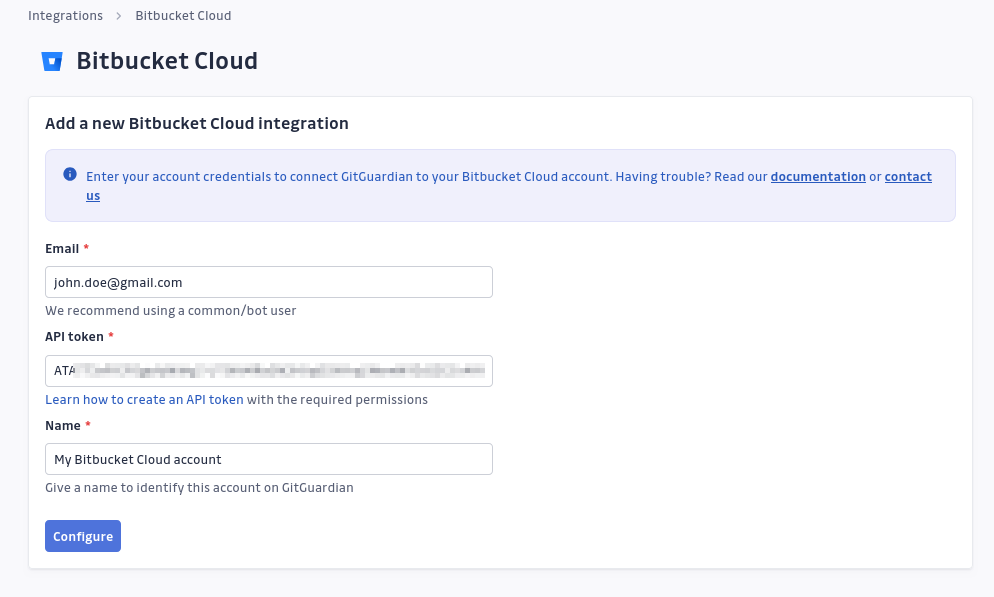
Enter the email from your Atlassian account and the API token generated earlier. Add a name for the integration, then click Configure.
-
On the configuration page, review the list of workspaces your Bitbucket Cloud user has access to. Click Install for each workspace you want to monitor.
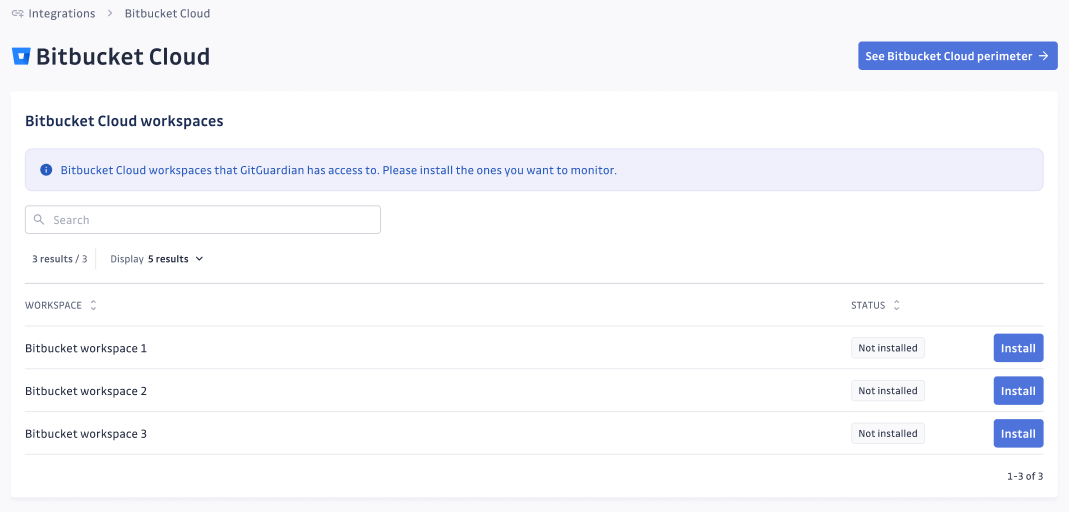
-
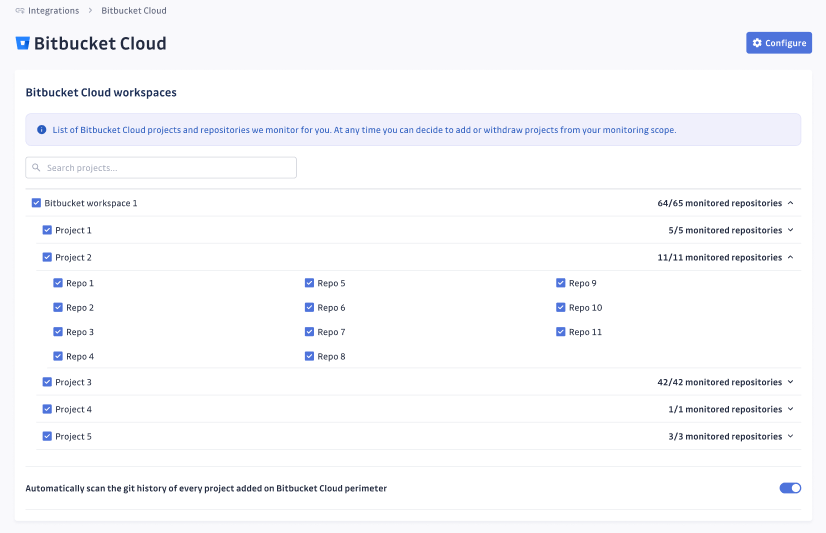
That's it! You can view the monitored projects and repositories in your Bitbucket Cloud settings page.
Automatic historical scan
By default, GitGuardian runs a historical scan on every Bitbucket Cloud repository added to the monitored perimeter.
To disable this feature, navigate to your Bitbucket Cloud settings. Only workspace Managers can modify this setting.
Understanding scanning capabilities
Historical scanning
Uncover your secret debt: When you first integrate this source, GitGuardian performs a comprehensive scan of your entire content history, based on your customized perimeter. This reveals secrets that may have been exposed weeks, months, or even years ago - helping you address your existing security debt.
Real-time scanning
Catch new exposures instantly: Once integrated, GitGuardian continuously monitors your content through event-based detection. Any new or modified content containing secrets are detected immediately, allowing you to respond quickly to new exposures.
Customize your monitored perimeter
After installing your Bitbucket Cloud instance(s), you can configure which projects to monitor in the Bitbucket Cloud settings.
If you deselect an entity (a repository, a project or a whole workspace) from your monitored perimeter:
- GitGuardian will stop fetching commits from that entity, new incidents will not be uncovered and existing incidents won't be updated for this entity.
- The webhook will remain active, allowing you to resume monitoring anytime.

