Integrate GitHub Enterprise Server
Monitor GitHub Enterprise Server repositories for exposed secrets in source files, configuration files, and commit histories.
GitHub Enterprise Server environments contain your organization's most valuable intellectual property and proprietary code. While self-hosting provides control, it also means you're responsible for detecting when developers commit production credentials, internal API keys, or infrastructure secrets that could compromise your entire enterprise network and applications.
Capabilities
| Feature | Support | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Historical Scanning | ✅ (Supported) | Complete repository history analysis |
| Real-time Detection | ✅ (Supported) | Instant detection via webhooks |
| Monitored Perimeter | ✅ (Supported) | Granular monitoring of your Orgs and repos |
| Team Perimeter | ✅ (Supported) | Team-based access control |
| Presence Check | ✅ (Supported) | Verify if secrets are still accessible |
| File Attachments | ❌ (Not Supported) | Not applicable for code repositories |
What we scan:
- Source code files, configuration files, and raw text files
- All repository branches and commit history
Setup
Prerequisites:
- Owner or Manager account on your GitGuardian Dashboard
- GitHub Enterprise Server admin permissions to install GitHub apps
- Network connectivity between GitGuardian and your self-hosted services. Check out GitGuardian Bridge to enable secure connections between GitGuardian SaaS and your self-hosted services in private networks.
GitGuardian integrates with GitHub Enterprise Server via a GitHub App with read-only access to your repositories.
By default, the GitGuardian GitHub app has only read access to your code. Optionally, it is possible to grant GitGuardian write access to benefit from specific business features (more detail in this dedicated section).
The pre-existing GitGuardian GitHub App cannot be leveraged to integrate with GitHub Enterprise Server. Instead, you will need to create a separate GitHub App on your own GitHub Enterprise Server instance. This process is straightforward since GitGuardian will automatically indicate the required configurations. You can refer to the GitHub documentation for more information on GitHub apps.
GitGuardian supports all GitHub Enterprise Server versions supported by GitHub itself.
Setup your GitHub Enterprise Server integration
- Navigate to Settings > Integrations > Sources.
- Click on Install for GitHub Enterprise Server.
- Enter the URL of your GitHub Enterprise Server instance, and select the permission level to grant to GitGuardian.
Read-only is sufficient to scan for incidents, while read and write permissions are necessary if you want to leverage business features such as Honeytoken deployment jobs.
The permission level can be changed later. See the dedicated section for more information.
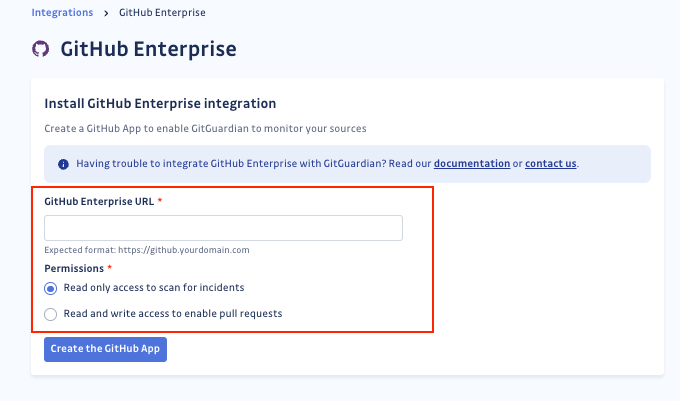 4. Click on Create the GitHub app to be redirected to GitHub Enterprise Server and create your dedicated app
4. Click on Create the GitHub app to be redirected to GitHub Enterprise Server and create your dedicated app
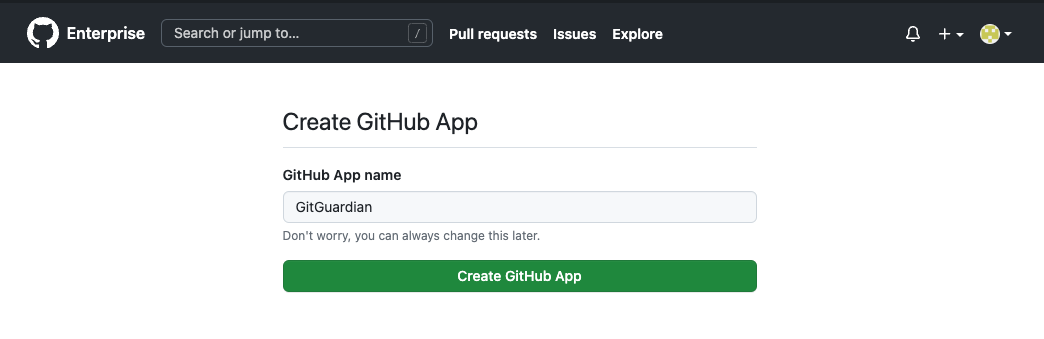
5. Validate the GitHub App creation. We recommend that you choose a simple name for your GitHub app such as GitGuardian, which will make it easily recognizable.
 6. The GitHub App is now created and you can install it for users and organizations.
7. Follow the exact same steps as for the GitHub.com SaaS integration.
6. The GitHub App is now created and you can install it for users and organizations.
7. Follow the exact same steps as for the GitHub.com SaaS integration.
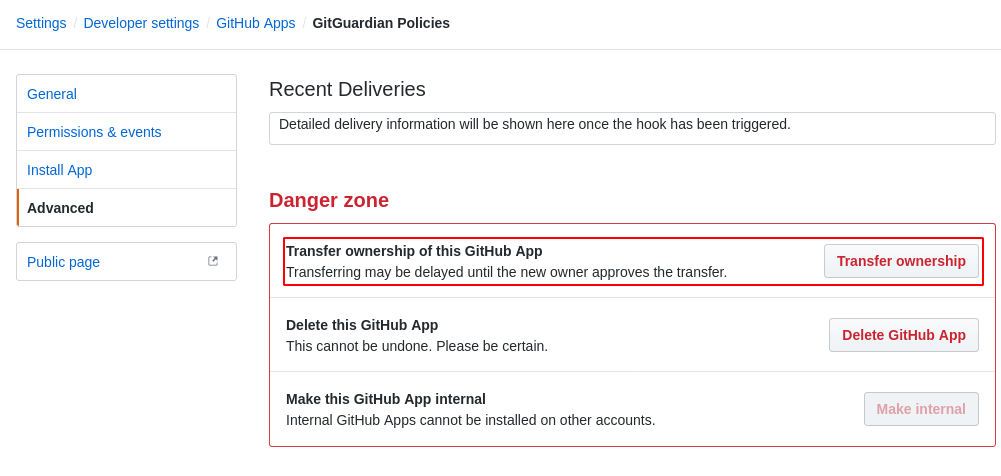
The GitHub App belongs to the user who created it. We recommend that you transfer the ownership to an organization in case the user is later deactivated.
IMPORTANT: GitGuardian cannot monitor repositories whose owner has not installed the GitHub App. If the repo is owned by a GitHub organization, the owner of the organization must install the GitHub App.
Configuration page
When you integrate your GitHub Enterprise Server instance, you have access to a configuration page.
From this page, you have the possibility to:
- integrate another GitHub Enterprise Server instance with GitGuardian.
- manage your existing instances and their dedicated GitHub app. GitGuardian tells you which ones are considered inactive.

Grant GitGuardian code write permissions
Some business features require write permission to your repositories in order to open pull requests.
Currently, this concerns the Honeytoken Deployment jobs feature.
If write permission was not provided at the time of app creation, you can grant this permission later by updating the existing app:
- In the configuration page, click "Configure write permission" for your GitHub Enterprise Server instance.
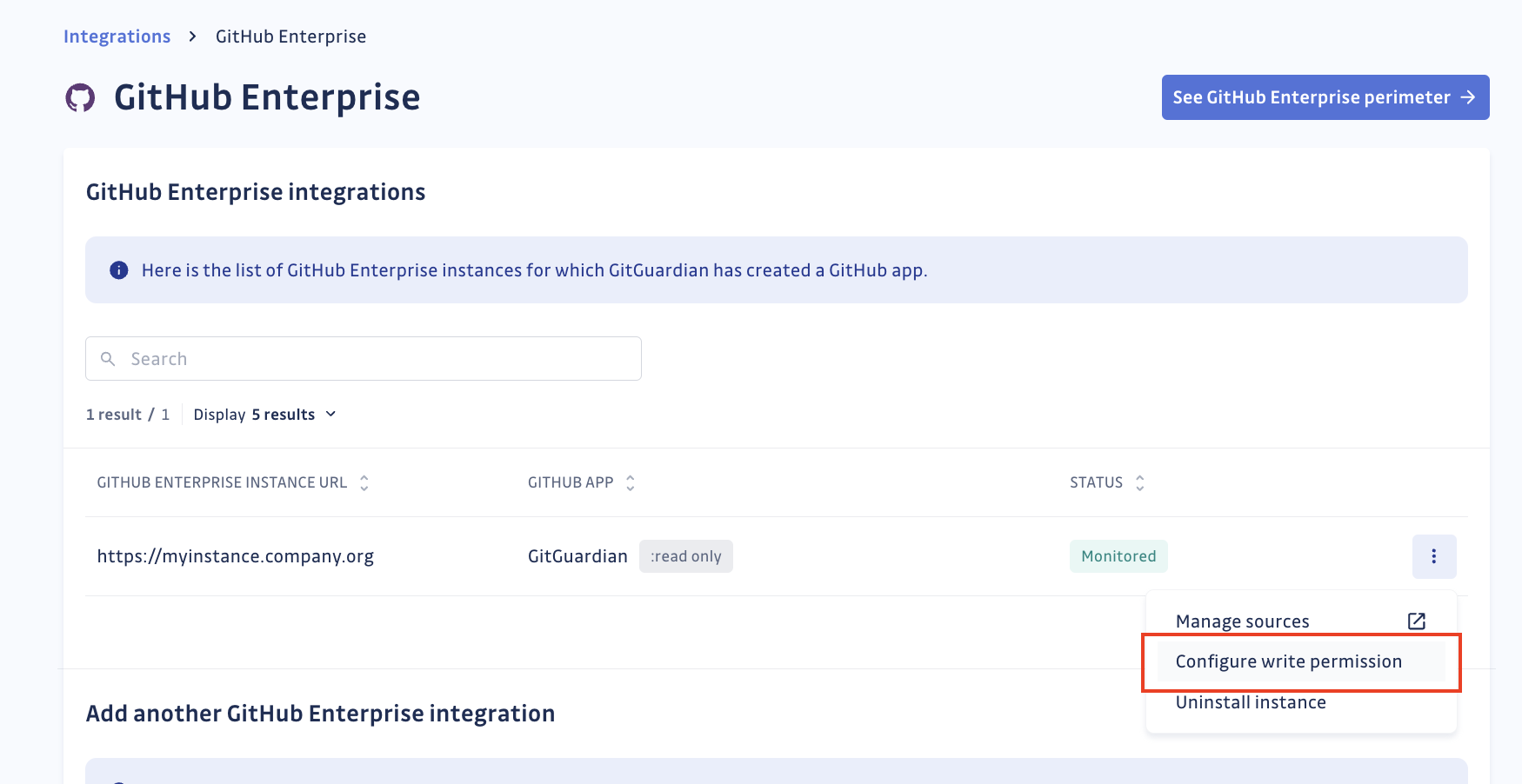
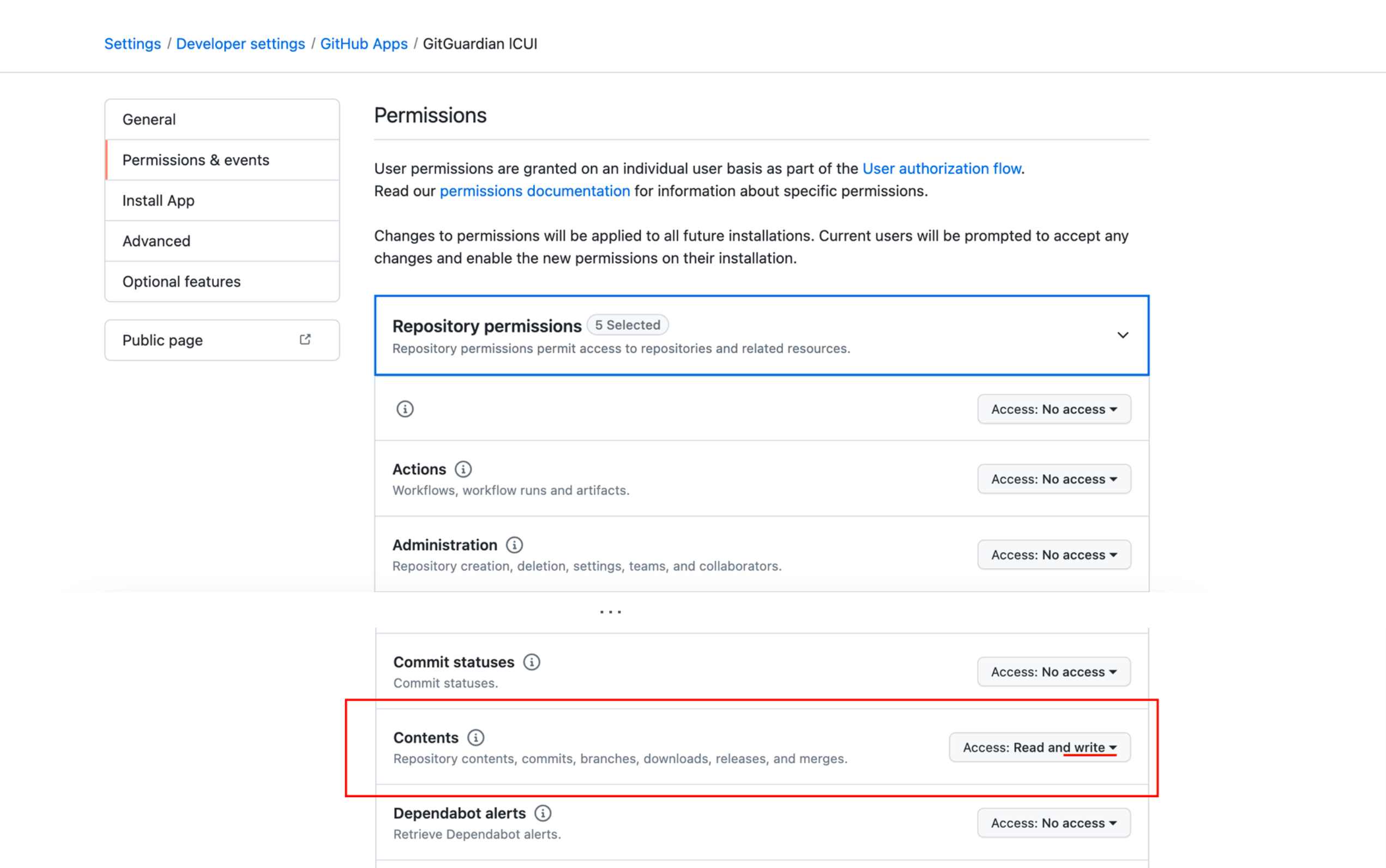
- You will be redirected to GitHub Enterprise Server, in the tab "Permissions & events" of the app. Under the "Repository permissions" section, change permissions on Contents to "Read and write":
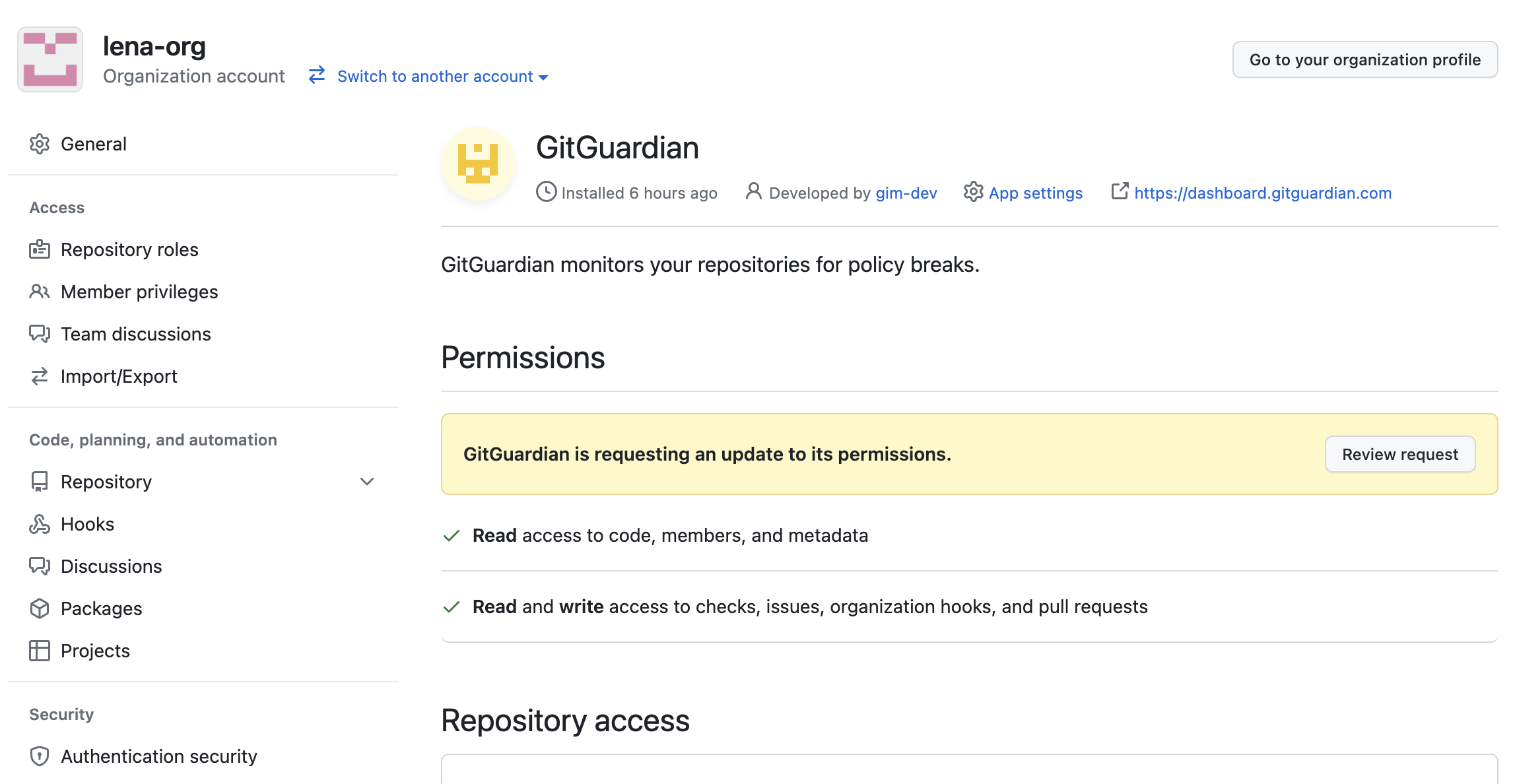
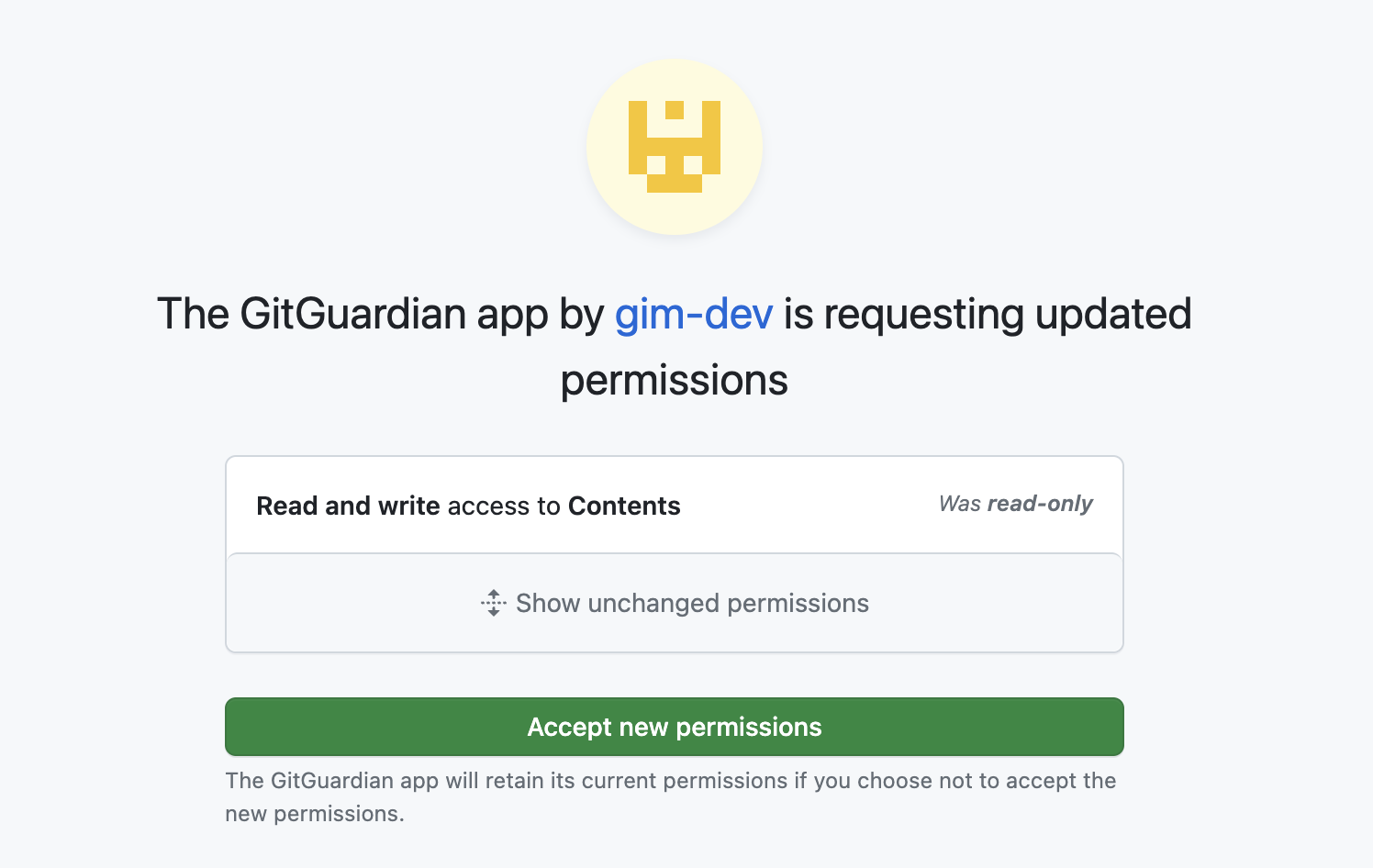
- This change then needs to be propagated to the organizations where this app is installed, by accepting the permission update request:
Automatic historical scan
By default, GitGuardian performs a historical scan for each newly created GitHub Enterprise Server repository added to your perimeter.
You can deactivate this behavior in your GitHub Enterprise Server settings if you are a Manager of the workspace.

Automatic repository monitoring
By default, GitGuardian automatically monitors repositories added to your perimeter.
You can deactivate this behavior in your GitHub Enterprise Server settings if you are a Manager of the workspace.

