Logs and debug
Viewing logs in pods
For a more interactive and user-friendly way to navigate Kubernetes pods and view logs, consider using k9s. This tool provides an efficient and visual way to manage Kubernetes applications directly from the command line, enhancing the experience of viewing logs and managing resources.
To view logs in a pod, use the kubectl logs command. Replace [POD_NAME] with the specific name of your pod:
kubectl logs [POD_NAME] -n [NAMESPACE]
If you're unsure of the pod's name, first list all pods with:
kubectl get pods -n [NAMESPACE]
Debug pod
Please note that to be able to run the debug command, your kubectl version must be >= 1.27.
To initiate a debug session for an existing pod, execute the kubectl debug command as shown below, using the internal-api pod as an example (replace [NAMESPACE] with the correct one and find the names of other pods on the Application topology page):
kubectl debug \
--namespace=[NAMESPACE] \
--profile=restricted \
--share-processes \
--container=app \
--copy-to=webapp-debug \
--image=$(kubectl --namespace=[NAMESPACE] get pods -l app.kubernetes.io/component=internal-api -o jsonpath='{.items[0].spec.containers[0].image}')-debug \
$(kubectl --namespace=[NAMESPACE] get pods -l app.kubernetes.io/component=internal-api -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
Where:
--profile=restricted: Mounts all volumes, config maps, and secrets from the original pod with limited capabilities.--container: Specifies the debug container.--copy-to: Names the new debug pod.--image: Sets the debug image, modifying the original image's tag with a--debugsuffix.
Upon execution, a debug pod named webapp-debug will be created in your designated namespace, containing a single app container running the debug image:
To interact with the debug container, use kubectl exec:
kubectl exec -it webapp-debug -- bash
For diagnostics, you may run:
kubectl exec -it webapp-debug -- python manage.py diagnose_instance
After completing your debugging tasks, remove the debug pod with this command:
kubectl delete pod webapp-debug
Log collector
Self-hosted GitGuardian deployments now feature a built-in log collector, designed to streamline troubleshooting and support. This system leverages Loki, MinIO, and Fluent Bit to automatically collect, store, and centralize logs from your GitGuardian application. Log collection is enabled by default for all installation types (Helm or KOTS), ensuring that all relevant logs are readily available for diagnostics without requiring manual configuration. By default, we retain 3 days of logs.
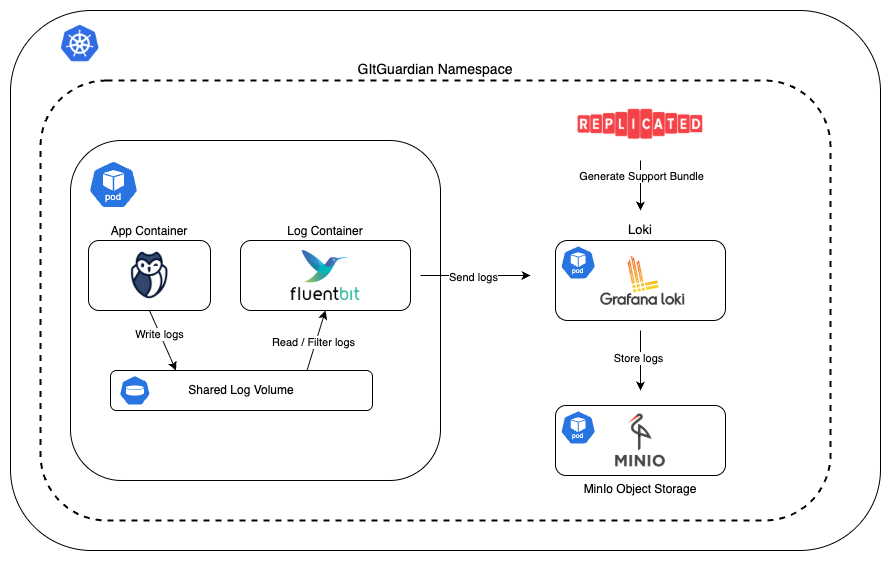
Helm-based installation
In the values.yaml file, set the logCollector.enabled parameter to false to deactivate the log collector.
By default, when generating the Support Bundle, we retrieve 3 days of application logs. This duration is configurable via the Helm parameter: logCollector.supportBundle.since using this format: <0-9>+<h|d>, and must not exceed 7 days.
Loki Configuration
You may need to configure Loki resource limits and pod labels to comply with your organization's policies:
Resource Limits:
loki:
singlyBinary:
resources:
limits:
# Specify CPU limits for Loki
cpu: 1000m
# Specify Memory limits for Loki
memory: 1024Mi
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
Pod Labels:
loki:
podLabels:
env: production
team: infrastructure
Additional pipelines
The LogCollector can be extended with custom pipelines to forward application logs to external log aggregation systems. This allows you to integrate GitGuardian's logs with your existing observability infrastructure.
Supported outputs:
The LogCollector leverages Fluent Bit's extensive output plugin ecosystem, enabling integration with popular log management platforms including:
- Splunk - Enterprise log management and analytics
- Loki - Grafana's log aggregation system
- Elasticsearch - Search and analytics engine
- Kafka - Distributed streaming platform
- Datadog - Cloud-based monitoring services
For the complete list of available outputs and their configuration options, refer to the Fluent Bit outputs documentation.
Configuration:
Additional pipelines are configured through the logCollector.pipelines section in your values file. Each pipeline can include:
- Filters - Transform, enrich, or modify log records before output
- Outputs - Define destination systems and connection parameters
Example: Splunk integration
The following configuration demonstrates how to send logs to a Splunk HTTP Event Collector (HEC) endpoint:
logCollector:
envFrom:
- secretRef:
# Secret containing token (SPLUNK_TOKEN)
name: splunk
pipelines:
splunk:
filters:
- |
name modify
add index my-splunk-index
outputs:
- |
name splunk
host <HOST>
port 8088
splunk_token ${SPLUNK_TOKEN}
tls on
tls.verify off
KOTS-based installation
In the KOTS Admin Console, deactivate the log collector.
Embedded cluster
In Embedded cluster, you need an additional step to be able to do kubectl commands.
sudo ./gitguardian shell
Now you can operate the cluster.
Worker Tasks
To monitor task activity, worker counts, and usage, visit the tasks page in the admin area.

