Choose your installation method
Before installing the application, you'll have to choose between these installation types:
- Existing Cluster using Helm (recommended) - for deployments on existing Kubernetes clusters using Helm charts (includes GCP Marketplace option),
- Embedded Cluster using KOTS - for all-in-one installations that create their own Kubernetes cluster with a web-based management interface.
This guide will explain the differences between these methods and help you decide which is the best for your needs.
What is Helm?
Helm is a package manager for Kubernetes, often referred to as the "Kubernetes equivalent of apt/yum/homebrew." It allows you to define, install, and upgrade even the most complex Kubernetes applications. Helm uses "charts," which are collections of YAML files that describe a related set of Kubernetes resources. This tool simplifies the management of Kubernetes applications by providing a single command to deploy an application, manage its lifecycle, and track version history. Helm configurations can be versioned in a Git Repository and integrate well with CD tools like ArgoCD or FluxCD.
FIPS (Federal Information Processing Standards) compliance is available exclusively for Helm-based installations. If you require FIPS-compliant cryptographic modules for regulatory compliance, you must choose the Helm installation method. For more details, see the Security Recommendations page.
GCP Marketplace
GitGuardian is also available on GCP Marketplace, Google Cloud's platform for discovering, deploying, and managing third-party software solutions. This enables deployment on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) clusters with consolidated billing through your GCP account.
The main benefits of GCP Marketplace deployment are consolidated billing through your GCP invoice, the ability to apply committed use discounts, and simplified procurement through existing GCP agreements.
The GCP Marketplace deployment uses Helm. The initial deployment is done through the GCP console, but upgrades and ongoing management are performed directly with Helm, this means you get all the benefits of Helm-based installations.
For more details, see the GCP Marketplace deployment guide.
What is KOTS?
KOTS (Kubernetes Off-The-Shelf) is a framework designed to help software vendors manage the lifecycle of Kubernetes applications in a way that’s user-friendly for enterprise customers. It provides a set of tools and a UI that simplifies the deployment, management, and support of Kubernetes applications.
What is an existing cluster installation
You can install the application on an existing Kubernetes cluster that already contains nodes using Helm. Ensure this cluster meets the system and network requirements.
The database preparation section will help you correctly configure them for your environment.
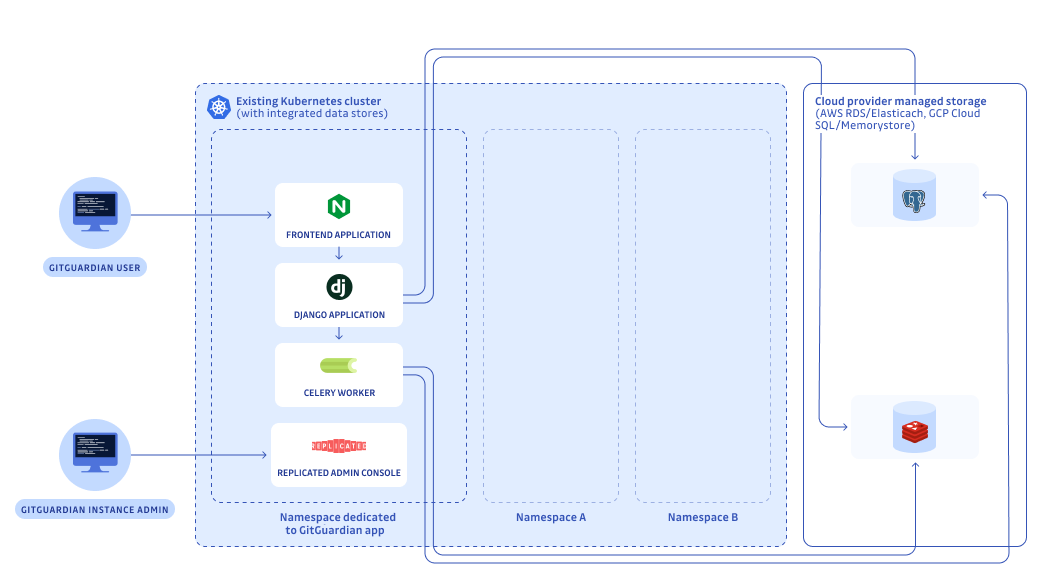
If you plan to install GitGuardian on an OpenShift cluster, please refer to the detailed guidelines for OpenShift cluster installation.
What is an embedded cluster installation
The Embedded Installation is an "all-in-one" installation where the Kubernetes cluster is created on your machine, and all components needed for the application are installed. This installation method uses KOTS (Kubernetes Off-The-Shelf) to provide a user-friendly web interface for deployment and management.
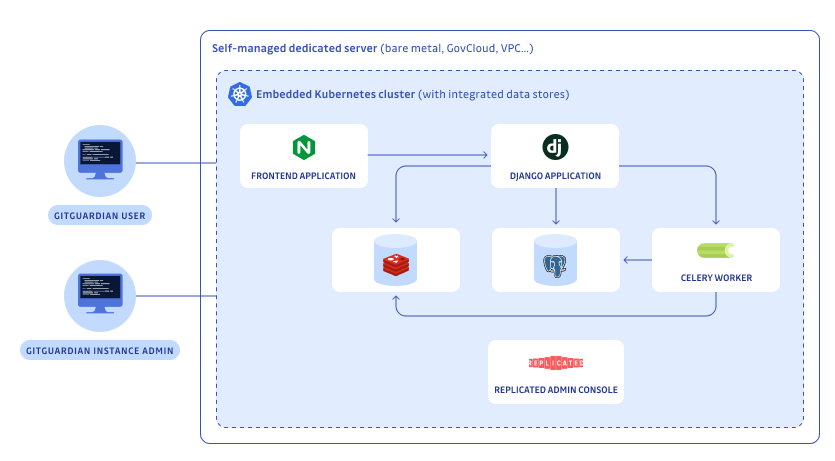
You can also use external databases to your embedded Kubernetes cluster (and we recommend it). The database preparation section will help you correctly configure them for your environment.
How to choose between these options
Before installing the application, you'll need to consider the following:
- do you possess the necessary resources and expertise to manage your Kubernetes cluster?
- do you have security policies in place in your Kubernetes cluster?
- do you have the expertise and resources to handle your own databases?
- will you require fine-tuning of the application?
If you already have a Kubernetes cluster, that is running different applications, with precise management and security policies and a dedicated maintainer in your teams, you should use the existing cluster installation using Helm. The application can be installed in a dedicated namespace for better isolation and organization. Please note you will also need access to Postgres database and Redis cache.
Helm installation offers extensive configuration options and integrates well with automation pipelines and Infrastructure as Code practices.
If you are deploying on Google Cloud Platform and want to consolidate billing through your GCP account, consider using the GCP Marketplace deployment. This allows you to use your GCP committed spend and simplifies procurement while leveraging GCP's managed services (Cloud SQL, Memorystore, GKE).
If you don't have resources dedicated to the maintenance of a Kubernetes cluster and databases, prefer the embedded installation, which uses KOTS to provide a user-friendly web interface for configuration and management. However, please note that embedded installations are not recommended for production use and are better suited for trial or Proof of Concept (PoC) purposes.
Feature matrix: Existing cluster (Helm) vs Embedded cluster (KOTS)
This feature matrix provides a comprehensive comparison between Helm installations (for existing clusters) and KOTS installations (for embedded clusters), highlighting their capabilities and key differences.
| Feature Name | Existing Cluster (Helm) | Embedded Cluster (KOTS) |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure as Code (IaC) deployment (recommended) | Yes | No |
| Graphical User Interface (GUI) deployment | No | Yes |
| Airgap deployment | Yes | Yes |
| Support OpenShift | Yes | Yes |
| External PostgreSQL and Redis (recommended) | Yes | Yes |
| Embedded PostgreSQL and Redis | No | Yes |
| Workload management (Replicas count) | Yes | Yes |
| Resources management (CPU/memory requests/limits) | Yes | Yes |
| HTTP Proxy | Yes | Yes |
| Custom CA | Yes | Yes |
| Load balancer + Ingress | Yes | Yes |
| ARM support | Yes | No |
| Ingress aware Architecture | Yes | No |
| Horizontal Pod Autoscaling | Yes | No |
| External log aggregation systems | Yes | No |
| Generic Ephemeral Inline Volumes | Yes | No |
| Node Affinity Scheduling | Yes | No |
| Istio service mesh | Yes | No |
| Set custom labels on pods | Yes | No |
| Existing Kubernetes secrets | Yes | No |
| Private Docker Registry | Yes | No |
| Deploy with ArgoCD | Yes | No |
| Deploy with FluxCD | Yes | No |
| FIPS | Yes | No |
| IPv6 | Yes | No |
| GCP Marketplace | Yes | No |

