Autoscaling
Requirements for autoscaling
You can use either Kubernetes HPA (Horizontal Pod Autoscaler) or KEDA (Kubernetes Event-Driven Autoscaler) for autoscaling. Both rely on the same metrics but have different requirements.
- HPA: Kubernetes built-in, reads metrics from Metrics Server or external metrics pushed by Prometheus Adapter. A bit less responsive than KEDA. Cannot scale to zero replica.
- KEDA: Reads events from a variety of sources (here Prometheus). Faster scaling. Can scale to zero replica. Not available on KOTS-based installations.
Required components
Depending on your chosen autoscaling method, you will need different components installed in your cluster:
| Component | HPA | KEDA |
|---|---|---|
| Prometheus server | Required | Required |
| Prometheus adapter | Required | Not required |
| KEDA controller | Not required | Required |
HPA requires Prometheus adapter to expose these metrics to the Kubernetes metrics API, while KEDA can directly query Prometheus.
Installing Prometheus server
If you don't already have Prometheus in your cluster, we recommend installing the standalone Prometheus server using the official Helm chart.
Add the Prometheus Community Helm repository:
helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo update
You can then proceed to install Prometheus:
helm install prometheus prometheus-community/prometheus \
--namespace monitoring \
--create-namespace \
--set alertmanager.enabled=false \
--set prometheus-pushgateway.enabled=false
The Prometheus server will be available at http://prometheus-server.monitoring.svc.cluster.local:80 (only reachable from within the cluster).
Installing Prometheus adapter
If you choose to use HPA for autoscaling, install Prometheus Adapter to expose Prometheus metrics to the Kubernetes metrics API.
helm install prometheus-adapter prometheus-community/prometheus-adapter \
--namespace monitoring \
--set prometheus.url=http://prometheus-server.monitoring.svc.cluster.local \
--set prometheus.port=80
See the Prometheus Adapter configuration section below for the rules to add.
Installing KEDA controller
Install the KEDA controller to enable autoscaling. You can install it using the KEDA Helm chart with the following commands:
helm repo add kedacore https://kedacore.github.io/charts
helm install keda kedacore/keda \
--namespace keda \
--create-namespace
You must configure the Helm values of your GitGuardian chart to allow KEDA to connect to your Prometheus server:
autoscaling:
keda:
prometheus:
metadata:
# Use the Prometheus server address from your installation
# Example with the prometheus-community/prometheus chart installed above:
serverAddress: http://prometheus-server.monitoring.svc.cluster.local:80
# Optional. Custom headers to include in query
customHeaders: X-Client-Id=cid,X-Tenant-Id=tid,X-Organization-Id=oid
# Optional. Specify authentication mode (basic, bearer, tls)
authModes: bearer
# Optional. Specify TriggerAuthentication resource to use when authModes is specified.
authenticationRef:
name: keda-prom-creds
A ScaledObject and an hpa will be created in the GitGuardian namespace.
Autoscaling workers
Autoscaling allows for dynamic scaling of worker pods based on Celery task queue length as an external metric for scaling decisions, improving efficiency and performance while optimizing resource costs.
To enable autoscaling based on Celery queue lengths, you need first to enable application metrics following this guide.
If you use KEDA, configuring the Prometheus adapter is not necessary.
Prometheus adapter configuration
Configure Prometheus adapter to expose Celery queue lengths as external metrics. This is done by setting up a custom rule in the Prometheus Adapter configuration.
The following rule should be added to your Prometheus Adapter Helm values to expose Celery queue lengths:
rules:
external:
- seriesQuery: '{__name__="gim_celery_queue_length",queue_name!=""}'
metricsQuery: sum(<<.Series>>{<<.LabelMatchers>>}) by (queue_name)
resources:
namespaced: true
overrides:
namespace:
resource: namespace
If you use Machine Learning, you will also need this rule:
rules:
external:
- seriesQuery: '{__name__="bentoml_service_request_in_progress",exported_endpoint!=""}'
resources:
namespaced: false
metricsQuery: sum(<<.Series>>{<<.LabelMatchers>>}) by (<<.GroupBy>>)
Autoscaling Behavior
The following behavior will be applied:
- Scaling Up: If the length of a Celery queue exceeds 10 tasks per current worker replica, the number of replicas will be increased, provided the current number of replicas is below the specified maximum limit.
- Scaling Down: If the number of tasks per current worker replica remains below 10 for a continuous period of 5 minutes, the number of replicas will be decreased, provided the current number of replicas is above the specified minimum limit.
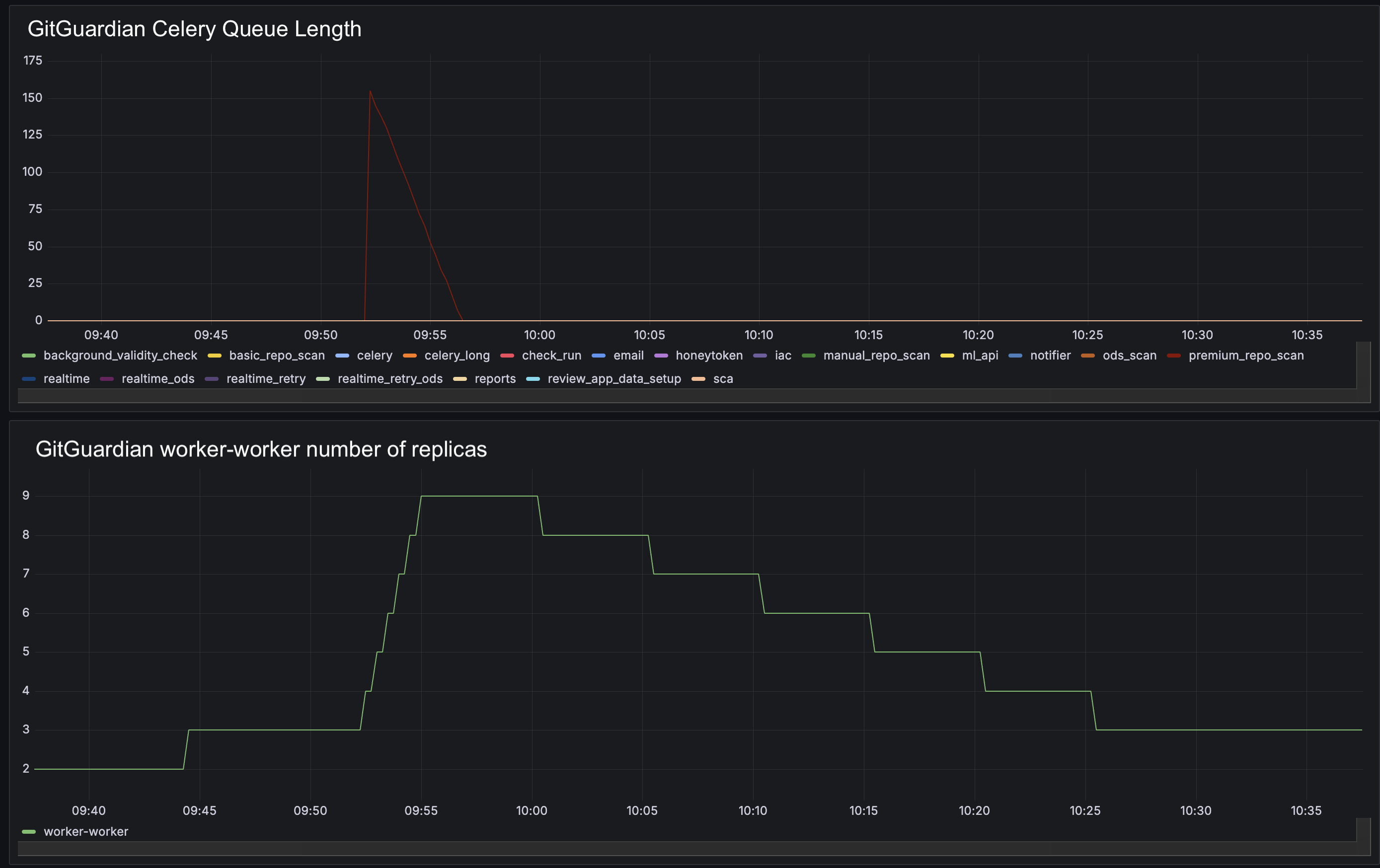
Using KEDA, when the Celery queue is empty, the worker will transition to an idle state, resulting in the number of replicas being scaled down to zero.
KOTS-based installation
KOTS-based installation only allows HPA autoscaling.
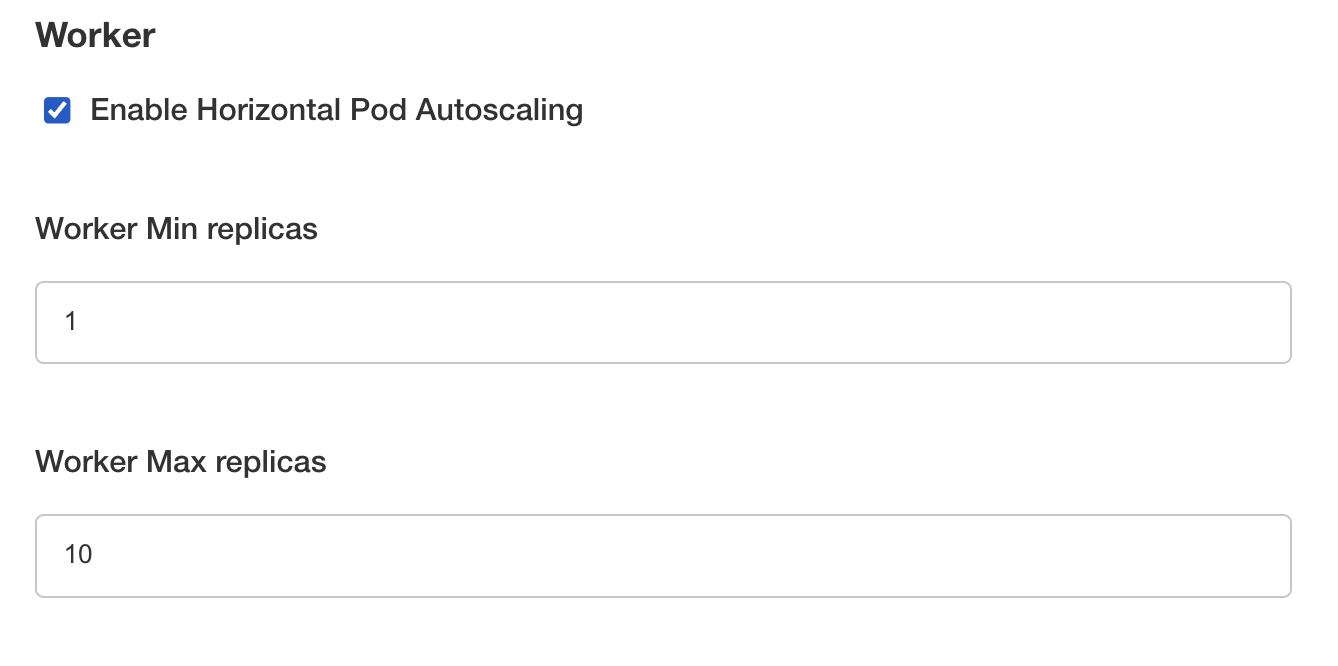
Navigate under Config > Scaling in the KOTS Admin Console, you will have access to the worker scaling options.
For each worker, you can enable autoscaling by ticking the option Enable Horizontal Pod Autoscaling, then you will be able to specify the minimum and the maximum replicas.
Helm-based installation
Customize Helm applications using your local-values.yaml file, submitted with the helm command.
Autoscaling Workers
You can enable worker autoscaling by setting the following Helm values (here, we enable HPA for the "worker" worker):
celeryWorkers:
worker:
autoscaling:
hpa:
enabled: true
keda:
enabled: false
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 10
Autoscaling the Machine Learning Secret Engine
For effective autoscaling of the Machine Learning Secret Engine, you must enable autoscaling for both:
-
The ML Worker processing the Celery queue (
ml-api-priority): this worker is responsible for queuing and dispatching ML-related tasks. Without autoscaling, it could become a bottleneck, leading to delays in processing requests. -
The Secret Engine handling the computation (
secretEngine): enabling autoscaling for the Secret Engine ensures that it can scale in response to the demand for ML computations.
To enable autoscaling, configure the following Helm values:
# ML Secret Engine
secretEngine:
autoscaling:
hpa:
enabled: true
keda:
enabled: false
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 2
celeryWorkers:
# ML Worker
ml-api-priority:
autoscaling:
hpa:
enabled: true
keda:
enabled: false
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 2
See the values reference documentation for further details.
autoscaling.hpa.enabled and autoscaling.keda.enabled Helm parameters are mutually exclusive, you must choose between hpa (using Prometheus adapter) and KEDA controller.

