Certificate-Based Authentication (legacy)
Certificate-based authentication is deprecated and will be removed in a future release. This feature is no longer actively maintained. If you are currently using this feature, please contact support@gitguardian.com to discuss migration options.
Certificate-based authentication requires users to present a TLS client certificate to authenticate with GitGuardian. This method is essential to authenticate using a Common Access Card (CAC) or Personal Identity Verification (PIV).
System Requirements
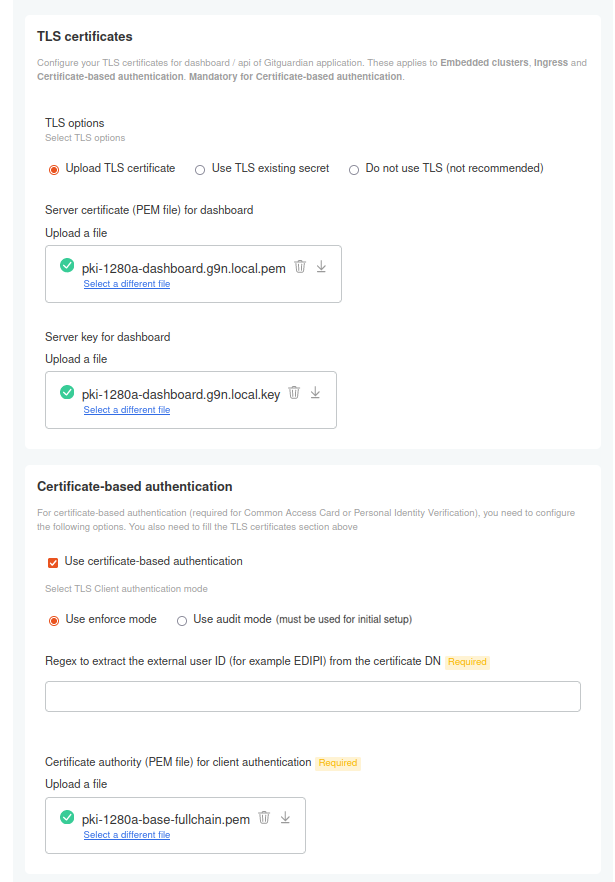
You will need a Certificate Authority (CA) in PEM format to set up client authentication. GitGuardian supports one or multiple CAs (a bundle) for this purpose. These CA(s) will be used to validate the client certificates required for authenticating to the GitGuardian dashboard.
Additionally, you must provide your own external user ID located in your client certificate, as well as the external user IDs of any users you want to invite to the GitGuardian platform. For example, the Department of Defense's Electronic Data Interchange Personal Identifier (EDIPI) found in the CN might look like C=FR,O=DGSE,CN=hubert.bonisseur.delabath.117 where the EDIPI = 117.
Network requirements
Outbound rules
To ensure proper communication with the OCSP or CRL server(s), please configure the following network rules:
| Port | Source | Destination | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 80 | All K8S nodes | your OCSP/CRL server(s) | OCSP/CRL server(s) |
Initial Setup
Follow these steps to configure certificate-based authentication in your self-hosted instance:
-
Initial Setup
- Follow specific instructions depending on whether you are installing GitGuardian in an embedded or existing cluster.
- Start with the mode set to
auditfor initial setup and verification. - Upload your CA that will validate client certificates.
- Configure the regular expression to extract the external user ID from the client certificate's subject (or use the default one if that works for you).
-
Authenticate for the first time
- Log in to your GitGuardian dashboard and provide your client certificate (or insert your CAC/PIV access card).
- If you encounter an error during authentication, an error page will appear with the reason for the failure (e.g., Certificate invalid, revoked, etc.). Note that this error page will only display in
auditmode.
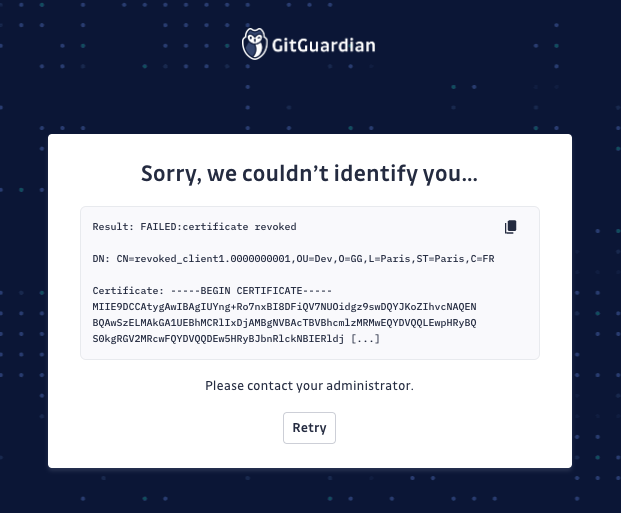
- If your client certificate is valid, proceed to login with your login/password to the GitGuardian dashboard.
- Then, enter the external user ID found in the CN of your client certificate when prompted.
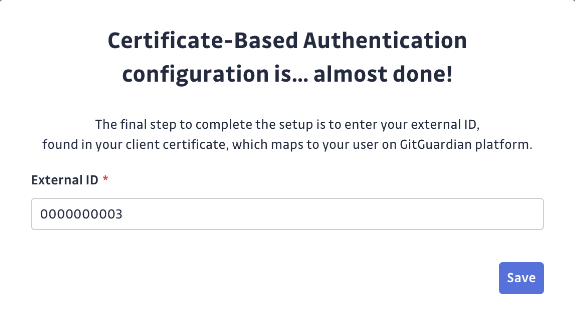
-
Verify and Enforce
- Navigate to the admin area under
Settings > Certificate-Based Authenticationto view client certificate and user mapping details.
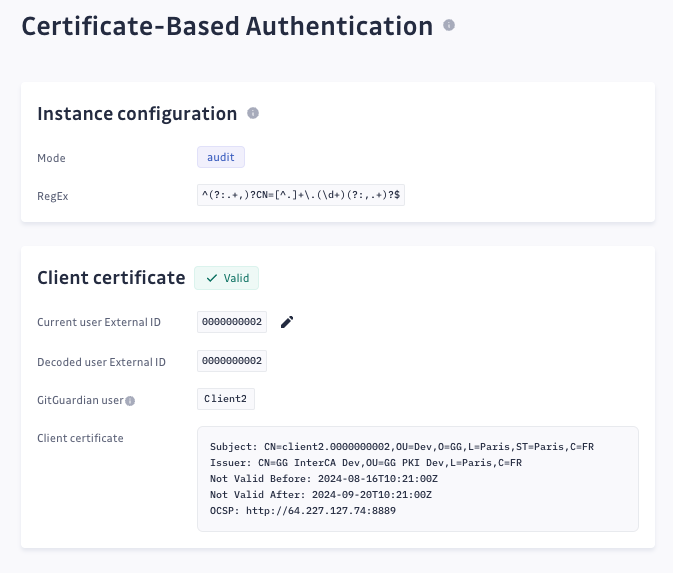
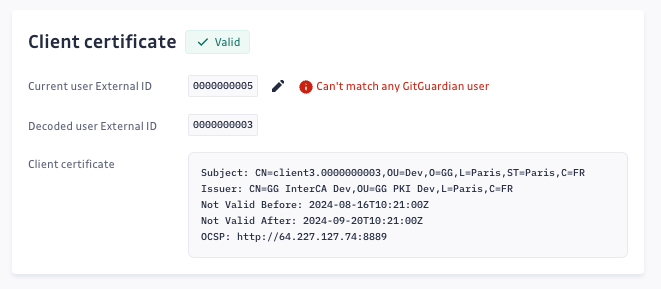
- If the external user ID is not properly associated with a GitGuardian user, an error message will be displayed. Ensure that the regular expression correctly extracts the user’s external ID and that the user ID is correctly configured.
- After confirming successful authentication and correct user mapping, switch to
enforcemode via KOTS or Helm. - Optional: You can enable email/password authentication or Single Sign-On (SSO) alongside certificate-based authentication. This provides an additional security layer and allows for scalable user management through SAML SSO.
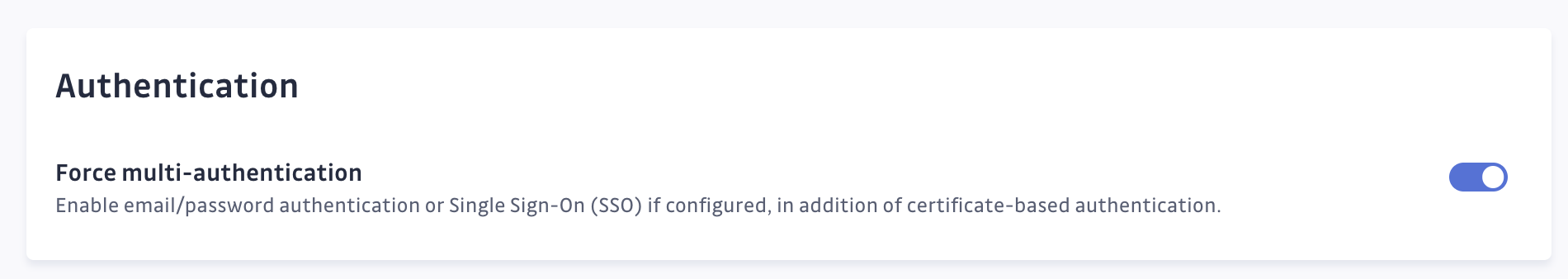
- Navigate to the admin area under
-
Integrate your first repositories and invite new user
- Integrate your first repositories to get started with automated secrets detection and remediation.
- Invite other team members along with their external user ID.
- ⚠️ Only users with admin area access can invite users by providing the external user ID. They can also modify it in the
Settings > Memberspage.
Configuration Parameters
For any installation (KOTS or Helm), configure the following parameters:
- Enable: Enable certificate-based authentication.
- Mode: Defines the application's behavior regarding client certificates.
audit: For setup only. Displays debugging information. ⚠️ Note: Public API routes are not functional with the audit mode.enforce: For production. Requires a client certificate.
- Certificate Authority: The CA that validates client certificates (also known as the CA bundle).
- CRL (optional): The certificate revocation list in PEM or DER format (OCSP used if not set).
- Regex: The regular expression to extract the unique user identifier from the certificate Distinguished Name (DN), part of the certificate's subject.
Existing Cluster
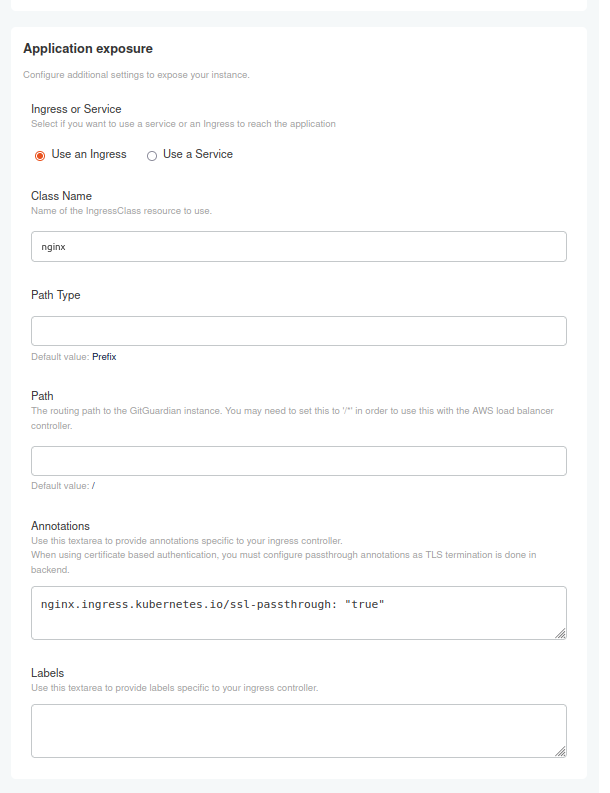
When you activate this option, TLS termination is done on the backend pods. Enable SSL passthrough based on your exposure method (Service Loadbalancer or Ingress). Examples are provided below.
KOTS-Based Installation
In the KOTS Admin Console, enable Use Certificate-Based Authentication and configure the parameters.
Helm-Based Installation
In Helm values, configure the following block:
tls:
clientAuth:
enabled: true
mode: enforce
userRegex: '(?:.+,)?CN=[^.]+\.[^.]+\.[^.]+\.(\d+)(?:,.+)?'
crt: ''
key: ''
caCrt: ''
ocspCacheSize: '10m'
existingSecret: ''
existingSecretKeys:
crt: 'server.crt'
key: 'server.key'
caCrt: 'ca.crt' # PEM format
crl:
url: ''
cron: '0 0 * * *'
persistence:
storageClass: ''
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
size: 1Gi
labels: {}
annotations: {}
Use existing secrets to store certificates.
Annotations Example
Service Loadbalancer on DigitalOcean
service.beta.kubernetes.io/do-loadbalancer-tls-ports: '443'
service.beta.kubernetes.io/do-loadbalancer-tls-passthrough: 'true'
Ingress Using NGINX Ingress Controller
ingress:
tls:
enabled: true
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-passthrough: 'true'
service:
port: 443
Add these in the annotations section of the KOTS Admin Console or in Helm values.
Notes about CRL usage in an existing cluster
You may choose to perform revocation checks using CRL instead of OCSP server. This mode :
- creates a Persistent Volume using a storageClass in the accessMode of your choice. This configuration depends on your cluster.
- fetches the CRL on a regular interval you define using a cron expression
Please reach out to our support team if needed.
Embedded Cluster
In the KOTS Admin Console, enable Use Certificate-Based Authentication and configure the parameters.

Troubleshooting
If you encounter authentication issues, switching to audit mode is recommended. To diagnose the problem, you can review the logs from the webapp-internal_api pod. For additional details, refer to our troubleshooting page.
To filter the logs for warnings, you can use the following command:
kubectl logs webapp-internal-api-6b98b7b9bc-wcvpb | grep warning
Common Issues:
- Invalid Client Certificate:
{
"timestamp": "2024-08-16T14:57:54.713592Z",
"level": "warning",
"event": "Mutual tls authentication failed",
"reason": "Missing or invalid certificate",
"remote_auth_result": "FAILED:certificate revoked",
"logger": "auth.mutual_tls.services.middlewares",
"gg_service": "ward-runs-app",
"gg_environment": "onprem",
"gg_version": "2024.8.0"
}
Solution: Verify the client certificate for validity. Check for issues such as expiration or revocation.
- External User ID Cannot Be Mapped to a GitGuardian User:
{
"timestamp": "2024-08-16T14:58:05.121226Z",
"level": "warning",
"event": "Mutual tls authentication failed",
"reason": "Invalid User",
"remote_user_dn": "CN=client3.0000000003,OU=Dev,O=GG,L=Paris,ST=Paris,C=FR",
"external_user_id": "0000000003",
"logger": "auth.mutual_tls.services.middlewares",
"gg_service": "ward-runs-app",
"gg_environment": "onprem",
"gg_version": "2024.8.0"
}
Solution: Ensure the regular expression correctly extracts the user’s external ID. Additionally, verify that the external user ID is properly associated with a GitGuardian user in the Settings > Members section of the GitGuardian dashboard. You must have admin privileges to access this setting.

