Ingress
Helm-based installation
In your values.yaml file, add the following extract, adapted to your needs:
ingress:
enabled: true
# -- Ingress controller in use in the cluster. Mandatory if using istio or `experimental.ingressRoutes=true`
# Supported: ingress-nginx / traefik / contour / aws_alb / openshift (Openshift Route) / istio
controller: 'ingress-nginx'
pathType: 'Prefix'
path: '/'
ingressClassName: 'my-class-name'
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: <ingress_class> # for ingress controllers that do not support ingressClassName
labels:
example.of.a.label: 'my-label'
tls:
enabled: true
existingSecret: 'secret-containing-the-ingress-tls-certificates'
istio:
# -- Istio revision, if any
revision: ''
gateway:
# -- Enable Istio gateway handling
enabled: false
# -- Istio Gateway name
name: ''
# -- Istio Gateway namespace
namespace: ''
# -- Istio Gateway selector
selector: 'ingressgateway'
See TLS certificate for help configuring TLS.
The experimental Ingress routes feature is deprecated. For existing users, see Legacy Ingress routes. New deployments should use the standard nginx-based routing.
KOTS-based installation
On existing clusters, a default Ingress is provided. This default Ingress is backed by a Kubernetes service (named gitguardian).
The default ingress is customizable, allowing modifications to className, pathType, Annotations/Labels.
TLS will be enabled if you upload a certificate in TLS certificates section.
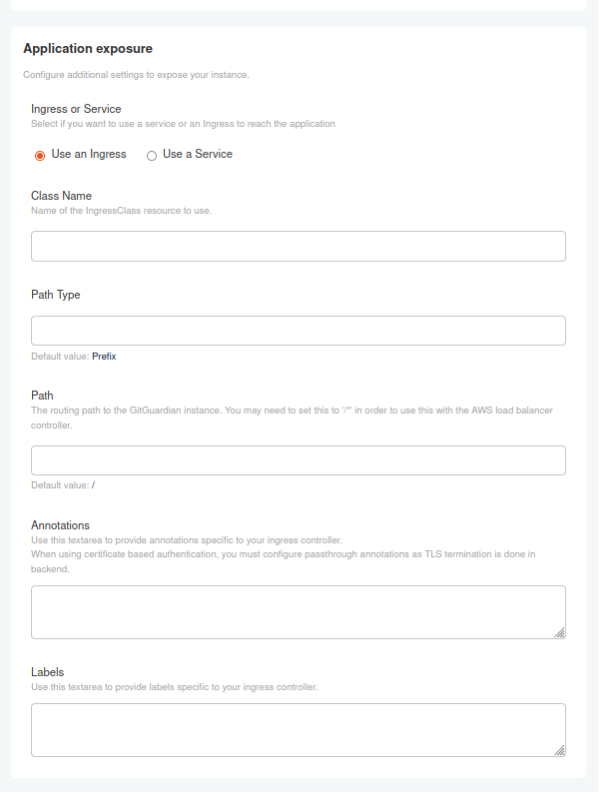
In the KOTS Admin Console, you may configure the following parameters:
- ClassName of the resource to use
- PathType and Path to route to the GitGuardian instance
- Annotations and Labels specific to your ingress controller
Using your own Ingress
You have the option to disable the default Ingress and set up your own. Here's how you can go about it based on your installation type:
Helm-based installation
In the values.yaml file, set the ingress.enabled parameter to false.
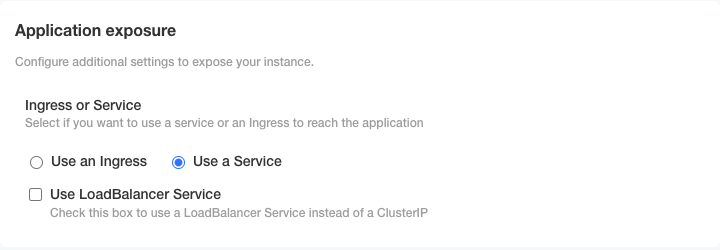
KOTS-based installation
In the KOTS Admin Console, simply use a Service.
Custom ingress configuration
If you opt to use your own Ingress, here are the fields you would need to modify:
defaultBackendingressClassName(use this for Ingress controllers that support it; otherwise, use the deprecatedkubernetes.io/ingress.classannotation)rulestls
To get more details on each of these fields, run the command kubectl explain ingress.spec.
Protocol configuration
The service backend is configured to listen only on HTTPS, and your Ingress needs to be set up accordingly.
If you are utilizing the NGINX Ingress controller, this configuration is already handled in the included Ingress through the nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: HTTPS annotation. However, if you are using a different Ingress controller, you may need to add the necessary annotations in the provided text area.
Sample configuration
Below is an example of how a custom Ingress configuration might look:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: <ingress_class> # for ingress controllers that do not support ingressClassName
labels:
kots.io/app-slug: gitguardian-seal
kots.io/backup: velero
name: gitguardian
namespace: <your-namespace>
spec:
ingressClassName: <ingress_class> # for ingress controllers that support this field
rules:
- host: <application_hostname>
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: gitguardian
port:
number: 443
path: /
pathType: Prefix
tls:
- hosts:
- <application_hostname>
secretName: <secret_name> # when using a kubernetes secret

